Recurrent neural networks, long short-term memory [13] and gated recurrent [7] neural networks in particular, have been firmly established as state of the art approaches in sequence modeling and transduction problems such as language modeling and machine translation [35, 2, 5]. Numerous efforts have since continued to push the boundaries of recurrent language models and encoder-decoder architectures [38, 24, 15].
Recurrent models typically factor computation along the symbol positions of the input and output sequences.
[info]
翻译:递归模型通常沿输入和输出序列的符号位置做计算。
有的材料把这里的“factor computation”翻译成因子计算,这是不对的。如果把“factor computation”看作一个词组的话,这句话就没有动词了。
Aligning the positions to steps in computation time, they generate a sequence of hidden states ht, as a function of the previous hidden state ht−1 and the input for position t.
[info]
翻译:将位置与计算时间中的时间步骤对齐,它们根据先前的隐藏状态ht-1和位置t的输入生成一系列隐藏状态ht。
This inherently sequential nature precludes parallelization within training examples, which becomes critical at longer sequence lengths, as memory constraints limit batching across examples.
[info]
翻译:这种固有的顺序性质阻止了训练示例中的并行化,这在较长的序列长度上变得至关重要,因为内存限制限制了样本之间的批处理。
[success]
原来以为RNN的并行化问题是指同一个样本的不同位置不能并行计算,实际上不是的!!!
RNN的并行化问题是指序列较长的情况下,Batch的size受到了限制。batch内的样本之间是可以并行计算的。size受到限制,就意味着一段时间内并行计算的样本数受到限制。
[warning]
[?] 仍然不明白的是,batch的size为什么会和sequence的长度有关呢?我个人认为,计算下一个时间步时,这一个时间步的信息就不需要了。所以一个样本所占的内存应该和只一个时间步所占的内存有关,与时间步的长度无关。
Recent work has achieved significant improvements in computational efficiency through factorization tricks [21] and conditional computation [32], while also improving model performance in case of the latter. The fundamental constraint of sequential computation, however, remains.
[success]
factorization tricks
conditional computation
这两种方法是通过提升样本间的并行性的方法来提升模型效率的。
Attention mechanisms have become an integral part of compelling sequence modeling and transduction models in various tasks, allowing modeling of dependencies without regard to their distance in the input or output sequences [2, 19]. In all but a few cases [27], however, such attention mechanisms are used in conjunction with a recurrent network.
In this work we propose the Transformer, a model architecture eschewing recurrence and instead relying entirely on an attention mechanism to draw global dependencies between input and output. The Transformer allows for significantly more parallelization and can reach a new state of the art in translation quality after being trained for as little as twelve hours on eight P100 GPUs.
[success]
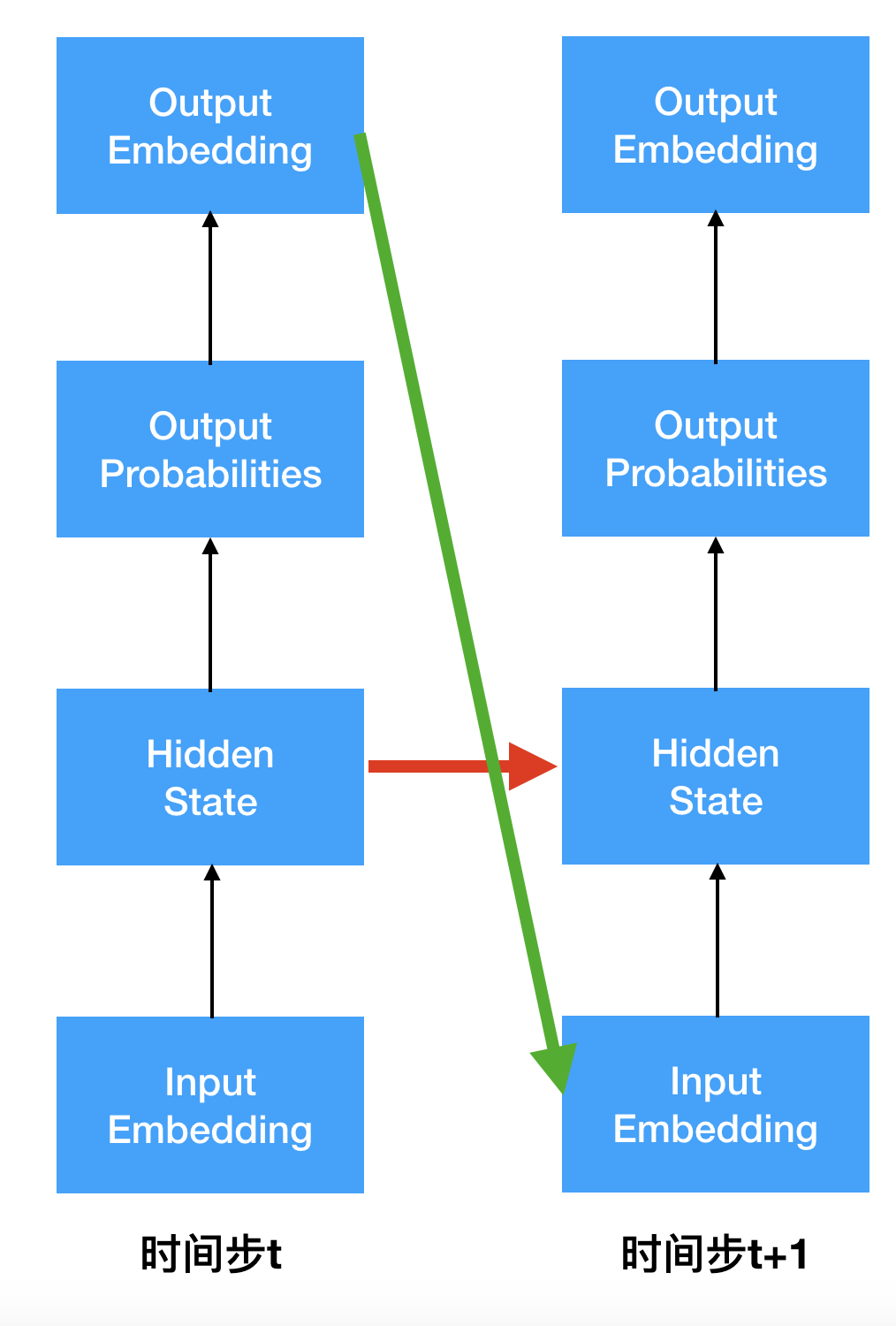
在Transformer之前,序列模型或序列转换问题普遍都是用基于gate和recurrent的网络结构。所谓的recurrent结构是指存在从当前时间步的hidden state流向下一个时间步的hidden state的数据流动。这种方法存在“并行性差”、“长距离依赖关系难以学习”等问题。
Transformer用Attention代替了传统序列转换问题模型中的recurrent结构。在“并行性差”的问题是缓解,解决了“长距离难以学习”的问题。 Transformer摒弃了recurrent结构,这不代表在Transformer中每个时间步之间没有关系。实际上在Transformer中,还是存在从当前时间步到下一个时间步的数据流动。下一个时间步使用了当时步的输出。
存在图上红线的路径才叫recurrent结构。Transformer中不存在红线路径,但仍存在绿线路径。